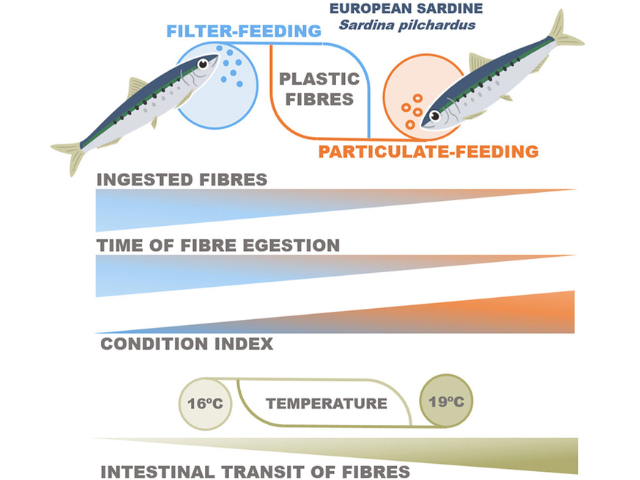
Feeding behavior and warming seas influence plastic fibre ingestion in sardines. Sardines that filter-feed ingest significantly more plastic fibres than those that eat larger particles (particulate-feeding). Warmer water temperatures (19°C) lead to faster digestion but also more plastic consumption. Filter-feeding sardines show lower health scores, highlighting the combined stress of microplastic pollution and climate change. (Source: Rodriguez-Romeu et al., 2024)
Sardines may be small, but they play a big role in the ocean—and on our dinner plates. These little fish are a key food source for larger marine animals like dolphins and tuna, and millions of people around the world eat them, too. They’re also packed with nutrients and are considered one of the most sustainable seafood choices out there.
But sardines are in trouble. In the Mediterranean Sea, their population has dropped sharply in recent decades. And scientists are discovering that two major forces—warming ocean temperatures and plastic pollution—are teaming up to make life even harder for these essential fish.
What’s harming sardines may be a warning sign for us all.
The Hidden Threat: Plastic Fibres in the Ocean
Microplastics are tiny pieces of plastic that break down from larger items like bottles, bags, and packaging. But not all microplastics are the same. A specific type called plastic fibres is even more common in the ocean—and more likely to be eaten by fish.
Plastic fibres are tiny thread-like pieces that come from clothing, fishing gear, and other waste. They’re too small to see with the naked eye but can float in the water, where fish easily mistake them for food. In fact, up to 91% of microplastics in ocean water are fibres, making them the most common type of plastic pollution in the sea.
The Experiment: What Scientists Found
To better understand how sardines interact with plastic fibres, scientists designed a unique experiment. They took wild sardines and placed them in tanks that mimicked ocean conditions. The tanks contained a realistic amount of plastic fibres—five fibres per liter of water, similar to what’s found in polluted areas of the sea.
They fed the sardines in two different ways:
- Particulate-feeding: Fish were given large food pellets, which they eat one by one.
- Filter-feeding: Fish were given tiny particles, similar to how they naturally eat plankton by filtering water through their gills.
The scientists also tested two water temperatures:
- 16°C, which reflects current Mediterranean conditions.
- 19°C, which represents a possible future scenario as oceans warm due to climate change.
Startling Results: What Happened to the Sardines
The results were clear—and concerning.
Sardines that fed by filter-feeding accidentally ate about eight times more plastic fibres than those eating larger particles. On average:
- Filter-feeders ingested 4.95 fibres per fish
- Particulate-feeders ingested only 0.6 fibres per fish
Temperature also made a difference. At warmer temperatures (19°C):
- Sardines expelled plastic fibres faster, likely due to faster digestion.
- But they also ingested more plastic, probably because their metabolism increased and they needed more food.
Another discovery: Plastic fibres stayed in the sardines’ digestive system longer than real food. Half the food was gone in about 12–14 hours, but it took 23–25 hours to get rid of just half the plastic fibres.
The Health Impact on Sardines
Over the course of the experiment, filter-feeding sardines didn’t just eat more plastic—they also got weaker.
- They lost more weight and had lower body condition scores compared to those eating larger particles.
- Their stomachs were less full, which suggests they ate less food overall and didn’t get enough energy.
Interestingly, the plastic alone wasn’t what made them unhealthy. Instead, it was the combination of filter-feeding and warmer water that seemed to hurt them most. Warmer oceans can lead to smaller plankton, which makes filter-feeding more common—and that leads to more plastic being ingested.
Why This Matters for Climate and Human Health
The health of sardines isn’t just a fish problem—it’s an ocean problem and a human problem.
Here’s why this matters:
- Warming oceans = smaller plankton
- Smaller plankton = more filter-feeding by fish
- More filter-feeding = more plastic consumed
If sardine populations continue to shrink:
- Predators like tuna, dolphins, and seabirds could lose a key food source.
- People who depend on sardines for protein or income may struggle.
- Ocean ecosystems could become unbalanced.
These changes don’t happen in isolation. Climate change and plastic pollution often work together, creating stress that marine life—and people—may not be able to overcome.
What Can We Do?
The good news is that small changes on land can protect life in the sea. Here are a few steps anyone can take:
- Choose clothes made from natural fibers (like cotton or wool). Washing synthetic clothes sheds plastic fibres into the water.
- Reduce plastic packaging by using reusable bags, bottles, and containers.
- Support ocean cleanup efforts and organizations that study microplastics.
- Advocate for climate action, including clean energy and reduced carbon emissions, to help slow ocean warming.
- Hold your local, state, and national elected officials accountable for taking climate action and protecting our water, air, and health.
A Call to Protect What Connects Us All
Sardines may not get much attention, but they’re part of a delicate chain that connects us all. When small creatures suffer, the effects can ripple through the food web—and onto our plates.
The choices we make on land ripple into the sea—and into our future.
By staying informed, reducing plastic use, and supporting climate action, we can help protect the ocean, our food systems, and the health of generations to come.
Source: Rodriguez-Romeu, O., Constenla, M., Soler-Membrives, A., Dutto, G., Saraux, C., & Schull, Q. (2024). Sardines in hot water: Unravelling plastic fibre ingestion and feeding behaviour effects. Environmental Pollution, 363, 125035. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0269749124017500