By Ben Welle, Rogier van den Berg and Claudia Adriazola-Steil, World Resources Institute (CC 4.0 International).
The coronavirus pandemic hit public transport hard. Global ridership tanked initially by as much as 80%, and transit was still at around just 20% of pre-pandemic ridership at the end of 2020. There is serious concern that people will increasingly opt for private vehicles, should public transport not recuperate.
Recent research by WRI shows how ensuring public transport not only survives but thrives is crucial for a green recovery, and to transport decarbonization actions that meet Paris Agreement goals.
Public transport is crucial to addressing climate change, equity and health
For the transport sector to help keep the 1.5 degrees C (2.7 degrees F) target of global warming in reach, high-income countries — which contribute 70% of global emissions and have high rates of motorization — will have to reduce vehicle travel, while developing economies will need to reduce or slow the growth of vehicle travel. The State of Climate Action report finds that the world needs to shift trips away from private vehicles between 4% and 14% compared to a business-as-usual scenario by 2030, even with strong progress on vehicle electrification.
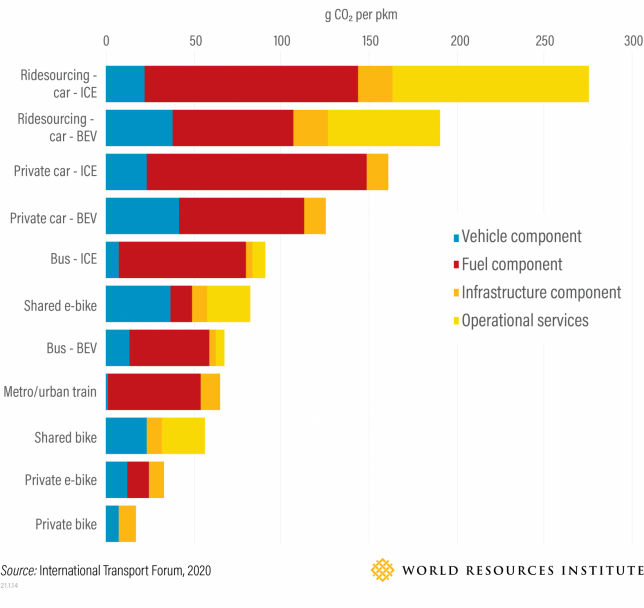
According to the International Transport Forum, buses and trains can release up to a fifth of emissions per passenger kilometer than ride-hailing and about a third that of a private vehicle. Simply put, public transport, along with bicycling and walking, is a climate solution staring us in the face. Embracing it in this next decade will be a determining factor in reaching climate goals.
Public transport is also key to an intersectional approach to addressing climate change in the transport sector — connecting with equity, health and economic development. When done well, it can provide more equal access to jobs, education, services and other economic opportunities, particularly to those without private vehicles and in underserved areas — all at a lower cost to consumers. The transit industry also provides millions of jobs globally that are important to local economies.
Other health challenges are also addressed through public transport: Cities with good public transport have fewer traffic fatalities. Transit riders tend to have more active lifestyles (from walking home from a station, station to work, etc.), and cleaner buses carrying more people than private cars can improve air quality and reduce exposure to dangerous pollutants in traffic.
Beyond the global pandemic shock — longer-standing challenges at play
Long before the coronavirus pandemic hit, public transport faced lack of investment and planning, unsupportive urban land use planning, and more recent challenges from disruptive technologies such as ride-hailing.
These historical challenges were often rooted in exclusionary policies based on race, class or gender, and favoring automobility over the needs of most of the public. For example, the United States subsidized the building of homes in car-oriented suburbia that excluded Black people and people of color through racial covenants, zoning and other ways while building freeways directly through their neighborhoods, displacing many and then cutting the public transit systems they relied upon.
This phenomenon is not limited to the U.S. and is often found across geographies that experienced colonialization (or some form of it). For example, in Nairobi, Kenya, history shows transport was built around the needs of European colonists, focused mainly on roads and not on public transport for all residents — perhaps carried on to today’s large expressway investments that continue to leave out the needs of low-income or marginalized people.
In Brazil, research suggests white and high-income people in cities have better transport access to opportunities than Black people and those with low-incomes, due to the location of housing and transport infrastructure. In many cases, even as some cities invest in a limited set of public transport projects, they simultaneously spend more money on private cars: take urban expressways like Mexico’s segundos pisos (elevated highways) and other projects in Latin America, or the many flyovers seen in Indian cities.
Meanwhile, public transport in many cities has been faced with an ever-present challenge to keep its riders despite limited public funding. Cities, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, tend to provide less operating support for their public transport systems. In Brazil, according to the National Association of Urban Transport Companies, ridership on public bus systems decreased by over 26% between 2013 and 2019 — in part because of policies promoting car and motorcycle purchases. And in India, public transport ridership has been stagnant, without vast improvements particularly in bus transit while residents take to private vehicles.
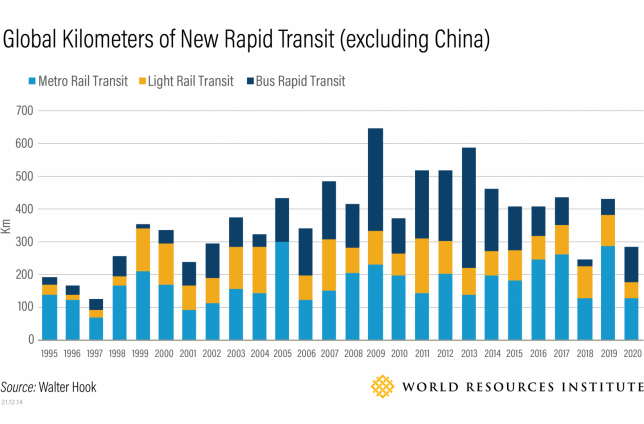
Another discouraging trend is that countries have been building less rapid transit. One recent analysis by Walter Hook found that the number of new kilometers of any form of rapid transit has fallen globally since 2013 (excluding the outlier of China) — including metro, Light Rail Transit and Bus Rapid Transit (BRT). Ride-hailing, or the use of apps to hail for-hire vehicles, may be one more recent contributor to the decline. Research from New York City shows that ride-hailing has added more congestion and emissions to city streets and is taking away from public transport.
For a variety of reasons, decision-makers have not yet made the necessary investments to address the equity and health issues outlined previously. This must change.
Making the case for putting public transport first
To set the world on a path to green recovery, doing so without public transport is a non-starter. The world needs countries and cities to make it a priority by stabilizing these services with vital support to ensure they survive, accompanied by plans, policies and finance.
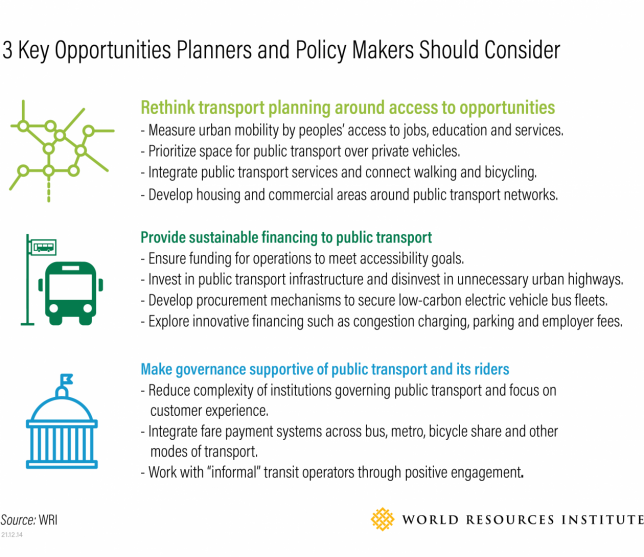
Here are three key opportunities for planners and policy makers to consider:
1. Rethink transport planning around access to opportunities
Cities should reshape how they plan and measure urban mobility — less on things like ridership and vehicle flow and more on how many residents have equal access to opportunities. This requires identifying areas where gaps in access exist and making targeted improvements in service such as frequency, reliability and capacity in those areas.
In many cities, as WRI research has shown, there are residents who do not have mobility and may be either underserved or trapped, for example in neighborhoods at the fringes of cities with extraordinarily long commutes. In fact, public transport is often not providing the service it could to low-income people. For example, in Mexico City someone living in one of the wealthiest neighborhoods has 28 times better access to jobs in a 30-minute trip by public transit and walking than those living in the poorest areas.
There are myriad measures that can help create an integrated public transport system that moves people more quickly to their destinations and reach those who have been denied access. We highlight a few key ways governments could consider revising their mobility plans in the wake of the pandemic:
Dedicate much more space to shared mobility. In some cities, streets can make up to 30% of land. A reallocation of these for public transport means dedicated bus lanes, for example, helping ensure high frequencies of service and reliability. Currently there are over 3,100 miles (5,000 kilometers) of documented bus priority corridors around the world and during the pandemic some cities laid down more bus-only lanes. Take New York City’s 14th Street busway which has improved travel times by closing the street to cars to prioritize the movement of people.
To scale to what’s needed, cities should ambitiously expand bus priority networks, as well as metro and Light Rail Transit where practical. One study from Sao Paulo found benefits of more direct transit routes for the many women domestic workers to their jobs in wealthier neighborhoods. These workers are some of the nearly 17 million women in Latin America who face long and divided commutes, as planners have instead focused on hub and spoke networks that are not responsive to female domestic workers’ mobility needs.
Avoid urban highways and improve reach of public transport. Take the well-known example in South Korea’s capital, Seoul, the Cheonggyecheon highway-to-linear park conversion; another part of the story is the city’s corresponding boost of its bus network as it shrunk its urban freeway footprint. According to a report on highway removal, the city expanded its network of median bus-only lanes to 42 miles, added several curbside bus-only lanes, coordinated schedules and fares to integrate with the subway system, and color-coded different services (local downtown buses, for example, are branded in yellow.) Within months, rider satisfaction had reached 90% and speeds in some bus corridors had improved up to 100%.
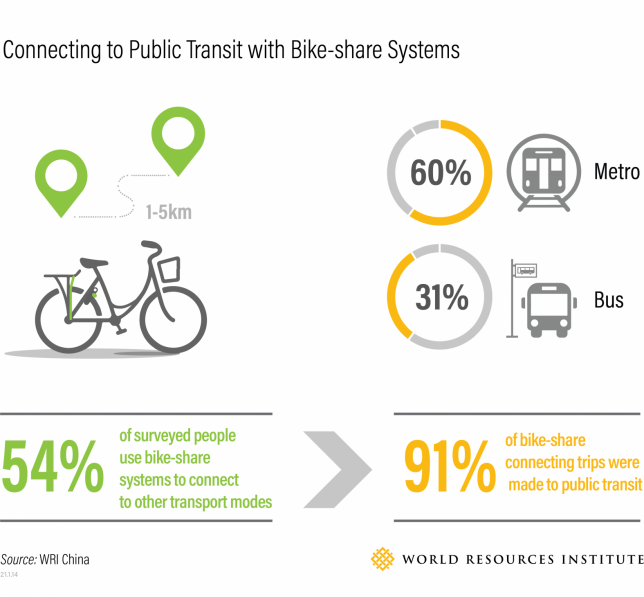
Connect with bicycling and walking measures. WRI China researchers found that in Chinese cities 54% of bicycle share users were using the service to reach other transport modes, including 91% of those riders connecting to public transit. If done right, bicycle and scooter share can be a great form of first and last mile connectivity. In addition, making streets and neighborhoods more human-oriented can make public transport one piece of a livable city’s pie. Just look at Paris, which according to the ITF, since 2014 has eliminated 15,000 parking spaces, expanded its bike network from 700 km to 1000 km, and converted riverbank expressways to public space, all while seeing the modal share for cars drop by 45% since 1990, cycling increasing tenfold, and, importantly, public transport use increasing by 30%.
Lastly, strategically place housing around public transport corridors. South Africa’s Johannesburg, for example, has been seeking to concentrate urban development near Bus Rapid Transit and trains as part of its Corridors of Freedom. The World Bank notes that from Singapore to Copenhagen, transit-oriented development has helped many cities reduce their carbon footprint while becoming more productive and more livable.
2. Provide sustainable financing to public transport
The million-dollar question is: how would all this be paid for? To help develop better public transport we need a change in how financing is provided, relying less on farebox revenue and more on public actors to provide robust and sustained financing for transit operations and capital investments. This includes funds to stabilize services during and coming out of the coronavirus pandemic-related shock.
But funding should not only support public transport just so it survives. Instead, new public sector support can set it on a sustainable financial path that allows it to thrive. Such commitments should be seen as investments that can reduce emissions, provide access to jobs, and improve health. Here are some key ideas how it can be done, and examples from around the world:
Provide steady revenue for operations. As many public transport systems do not receive sustainable government support for operations, national governments could step in with more support, in turn improving contracts with operators or increasing service to underserved areas. Providing sustainable operating funds may require diversifying the sources of funding, so that fare revenue is just one piece of a multi-piece pie.
In Vienna, Austria — a city which has grown its public transport usage over the last decade — while user fares cover about 55% of transit operating costs other sources include: indirect payments from the national government; a public transport tax on large employers; and fees from on-street parking and city-owned parking garages. One promising proposal from the national government in India would not only finance acquisition of over 20,000 buses, but could also support operations. More of these new or revamped financing options will be necessary, and governments can use the added support to require improved access, services or contracting.
Renew investment in public transport infrastructure. Over a decade ago, governments in several middle-income countries established mass transit national programs — such as Mexico’s Public Transportation Federal Support Programor India’s National Urban Renewal Mission, that have funded the expansion of Bus Rapid Transit and bus services as well as subways. Some of these programs have fallen by the wayside, and a revival of national investments is needed to expand rapid transit infrastructure to address climate, health and equity needs. Nevertheless, cities can act now by directing their existing road maintenance budgets to close areas or lanes to cars and repaint the streets for public transport, walking and cycling. Congestion charges are another way to provide revenue for a wide-scale city level repositioning of surface transport. In London, for instance, over £1.3 billion in such revenue was dedicated over 14 years to improving the bus network, and the results were impressive. From 2002 to 2018, the percentage of trips made by private car in the city shrunk from 46% to 36%, while public transport grew from 29% to 37%.
Package financing to make public transport an all-electric service. Public transport has been partly electric for well over 100 years with the introduction of electric tramways in the 1880s. However, today most buses remain powered by internal combustion engines. Electrifying public bus fleets globally could not only help reduce emissions but greatly improve services and health. Electric buses are also less costly to run, with lower total capital and maintenance costs. Despite barriers — including higher upfront costs and the need for charging infrastructure — programs such as those from China and Chile have shown how governments can support the procurement of these buses where operators may not have previously been able to fully cover them. WRI, together with the Transformative Urban Mobility Initiative and other partners are assisting 20 cities in creating electric bus fleets and scaling e-bus adoption to hundreds more through city-to-city mentorship, including addressing these financial barriers.
3. Make governance supportive of public transport and its riders
The story, however, is not all about infrastructure and money. Cities need better institutions and governance to plan, manage and implement improved public transport. This includes creating more cohesive and professional transport authorities and integrated systems, and changing the way so-called “informal transit” is included from one of displacement to replacement.
Govern transport through better institutions. Now, every city may have a different context and solution, but there are a variety of ways to create better institutions. Take the Sao Paulo metro area in Brazil, where there are 39 cities with 39 different mayors and a state government running inter-city rail. Cutting down on this complexity can result in better service to users and improve efficiency. In some cities, there may be a need for a unified metropolitan transport authority that can plan and manage the entire system.
Transport for London (TfL), for example, was formed in 2000 by combing nearly all agencies responsible for transport — primary roads, streetscapes, rail, bus, cycling and taxi provision. The new organization model was tasked with showing results for people, rather than the needs of a specific mode of transport, and as such TfL has implemented coordinated changes to bring about fundamental transformation. Congestion pricing was possible in part due to the efficient reorganization and promotion of bus services. Fare capping methods, which limits upfront and monthly costs to the user over time, required a holistic view of transport revenues across the region.
While a combined transport agency may not be appropriate for any context, other cities such as Lagos, Nigeria, have established authorities to focus on public transport. And several cities across the globe have increased government planning and contracting, establishing public transport agencies that reform contracting and offer improved branding and service planning. Governments need to revisit and continue advancing better models.
Integrate fare payment systems. One of the more important ways cities can improve integration is through unified fare card systems. These not only improve the customer experience but enable better integration among multiple providers of public transport. In Istanbul, Turkey, the Istanbulkart is part of an integrated fare payment that previously constituted some 17 different payment forms across 11 different agencies, and can now be used at over 17,000 points in the city, including buses, metro, ferries, cable cars and even parking. Fare cards can now also be offered in mobile phone apps: In Delhi, India, a pilot program for an app-based payment was put into place with positive response from riders last year, and the city opted to scale up the option citywide.
Work with the “informal” transit that carries many if not most people. This may require a shift away from measures that often seek to displace minibus operators — those that run popular, informal transit in many cities around the world — with a non-punitive approach that supports improved business models, labor conditions for workers, data collection and analysis, and quality of service. Kigali, Rwanda has introduced more formal public bus services through three companies that are under contract with the Rwanda Utilities Regulatory Authority. In Cape Town, South Africa, after the Bus Rapid Transit was introduced in 2010 with less than expected ridership due in part to lack of integrated minibus systems, the city has been supporting better integration of the minibuses to run alongside the BRT.
The time to act for climate and people
When we say we need to reimagine public transport, we are speaking to the need not to reinvent it, but to transition how we plan, fund and govern it to be the backbone of mobility in cities.
Beyond some of the items outlined above, there may be other actions necessary to improve quality — such as communicating that public transport is safe to ride and improving marketing and branding, ensuring more can afford to ride and efficiencies of route planning. A lot will depend on the context of each city or country.
Importantly, countries need to increase their policy commitments under the Paris agreement through enhancing and updating their national climate action plans and Long-Term Strategies. This is where countries can lay down their commitments to connect public transport to climate action. Many current climate action plans do not even address urban transport, and the German Corporation for International Cooperation found that none of the recent updates declare national government support for cities to finance change.
We have no small task ahead. Rebooting public transport will require the support of a cadre of global stakeholders — including development banks, national governments, state and local officials, researchers, development aid institutions and philanthropy and companies. We’re calling on the world to act and to not forget this essential element in addressing climate change. These actors should come together on a new set of principles for reimagining public transport and move forward to enacting this agenda. The world cannot wait, and neither can the people who need better access, every day, to the jobs and city services that can improve their lives and well-being.