By, Sonja Klinsky, The Conversation (CC BY-ND 4.0).
Climate change has hit home around the world in 2021 with record heat waves, droughts, wildfires and extreme storms. Often, the people suffering most from the effects of climate change are those who have done the least to cause it.
To reduce climate change and protect those who are most vulnerable, it’s important to understand where emissions come from, who climate change is harming and how both of these patterns intersect with other forms of injustice.
I study the justice dilemmas presented by climate change and climate policies, and have been involved in international climate negotiations as an observer since 2009. Here are six charts that help explain the challenges.
Where emissions come from
One common way to think about a country’s responsibility for climate change is to look at its greenhouse gas emissions per capita, or per person.
For example, China is currently the single largest greenhouse gas emitter by country. However, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, the U.S., Australia and Canada all have more than twice the per capita emissions of China. And they each have more than 100 times the per capita emissions of several countries in Africa.
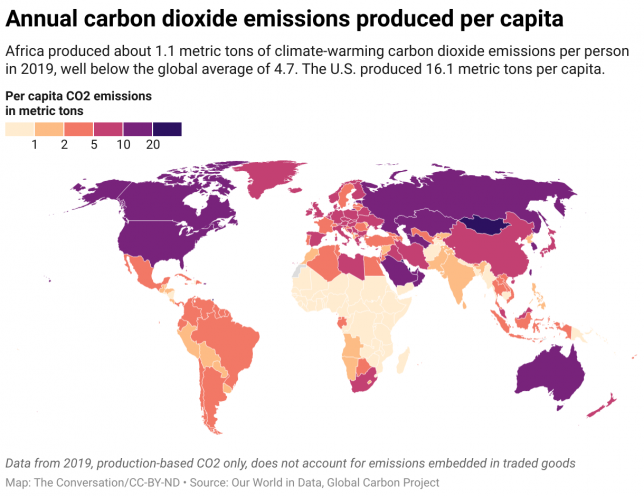
These differences are very important from a justice perspective.
The majority of greenhouse gas emissions come from the burning of fossil fuels to power industries, stores, homes and schools and produce goods and services, including food, transportation and infrastructure, to name just a few.
As a country’s emissions get higher, they are less tied to essentials for human well-being. Measures of human well-being increase very rapidly with relatively small increases in emissions, but then level off. That means high-emitting countries could reduce their emissions significantly without reducing the well-being of their populations, while lower-income, lower-emitting countries cannot.
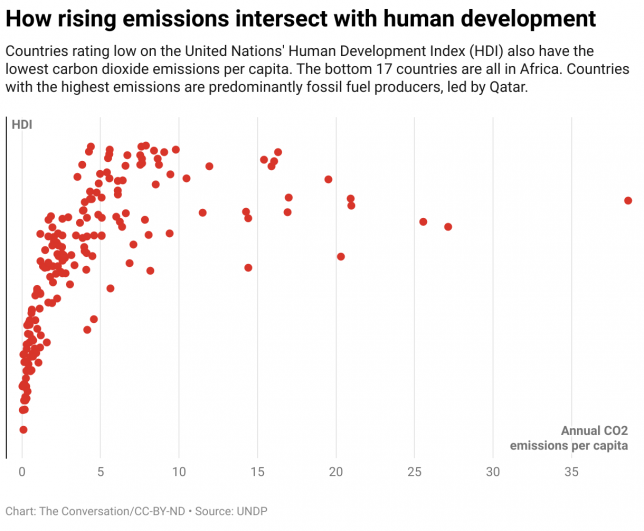
Low-income countries have been arguing for years that, in a context in which global emissions must be dramatically reduced in the next half-century, it would be unjust to require them to cut essential investments in areas that richer countries already have invested in, such as access to electricity, education and basic health care, while those in richer countries continue to enjoy lifestyles with high consumption of energy and consumer goods.
Responsibility for decades of emissions
Looking at current emissions alone misses another important aspect of climate injustice: Greenhouse gas emissions accumulate over time.
Carbon dioxide stays in the atmosphere for hundreds of years, and this accumulation drives climate change. Carbon dioxide traps heat, warming the planet. Some countries and regions bear vastly more responsibility for cumulative emissions than others.
For instance, the United States has emitted over a quarter of all greenhouse gases since the 1750s, while the entire continent of Africa has emitted only about 3%.
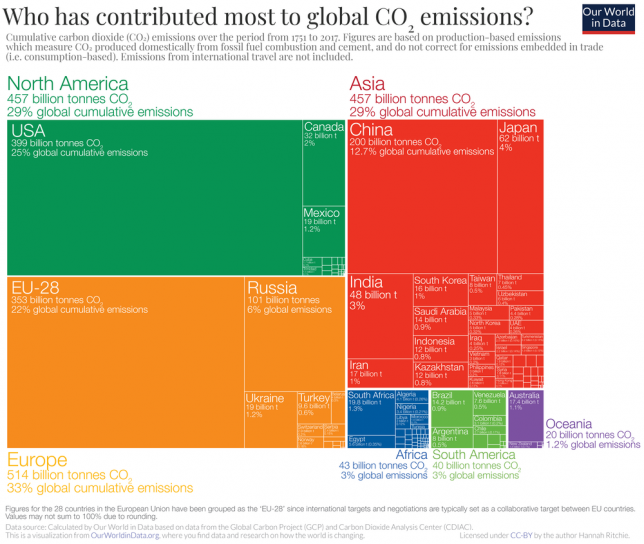
People today continue to benefit from wealth and infrastructure that was generated with energy linked to these emissions decades ago.
Emissions differences within countries
The benefits of fossil fuels have been uneven within countries, as well.
From this perspective, thinking about climate justice requires attention to patterns of wealth. A study by the Stockholm Environment Institute and Oxfam found that 5% of the world’s population was responsible for 36% of the greenhouse gases from 1990-2015. The poorest half of the population was responsible for less than 6%.
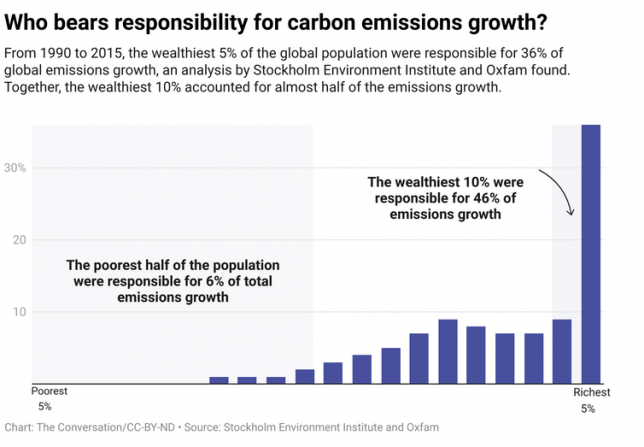
These patterns are directly connected to the lack of access to energy by the poorest half of the world’s population and the high consumption of the wealthiest through things like luxury air travel, second homes and personal transportation. They also show how actions by a few high emitters could reduce a region’s climate impact.
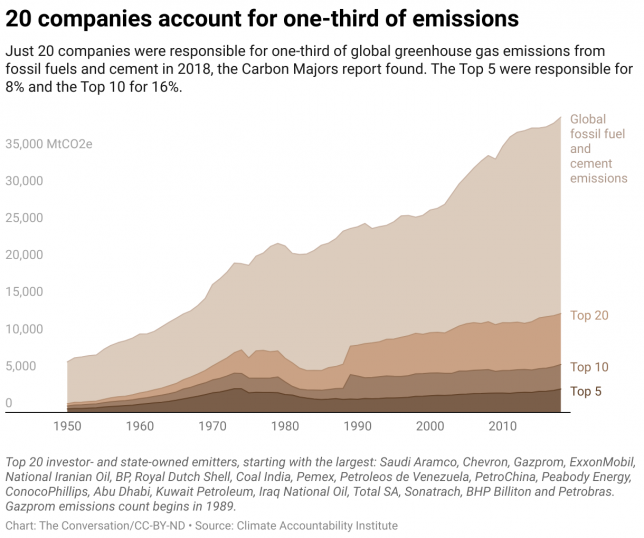
Similarly, over one-third of global carbon emissions from fossil fuels and cement over the past half-century can be directly traced to 20 companies, primarily producers of oil and gas. This draws attention to the need to develop policies capable of holding large corporations accountable for their role in climate change.
Who will be harmed by climate change?
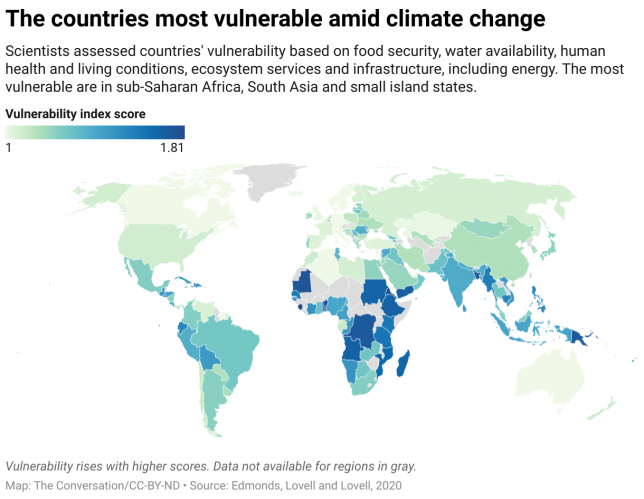
Understanding where emissions come from is only part of the climate justice dilemma. Poor countries and regions often also face greater risks from climate change.
Some small island countries, such as Tuvalu and the Marshall Islands, face threats to their very survival as sea levels rise. Parts of sub-Saharan Africa, the Arctic and mountain regions face much more rapid climate change than other parts of the world. In parts of Africa, changes in temperature and precipitation are contributing to food security concerns.
Many of these countries and communities bear little responsibility for the cumulative greenhouse gas emissions driving climate change. At the same time, they have the fewest resources available to protect themselves.
Climate impacts – such as droughts, floods or storms – affect people differently depending on their wealth and access to resources and on their involvement in decision making. Processes that marginalize people, such as racial injustice and colonialism, mean that some people in a country or community are more likely than others to be able to protect themselves from climate harms.
Strategies for a just climate agreement
All of these justice issues are central to negotiations at the United Nations’ Glasgow climate conference and beyond.
Many discussions will focus on who should reduce emissions and how poor countries’ reductions should be supported. Investing in renewable energy, for example, can avoid future emissions, but low-income countries need financial help.
Wealthy countries have been slow to meet their commitment to provide US$100 billion a year to help developing countries adapt to the changing climate, and the costs of adaptation continue to rise.
Some leaders are also asking hard questions about what to do in the face of losses that cannot be undone. How should the global community support people losing their homelands and ways of life?
Some of the most important issues from a justice perspective must be dealt with locally and within countries. Systemic racism cannot be dealt with at the international level. Creating local and national plans for protecting the most vulnerable people, and laws and other tools to hold corporations accountable, will also need to happen within countries.
These discussions will continue long after the Glasgow conference ends.
Sonja Klinsky, Associate Professor and Senior Global Futures Scientist, Arizona State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
This story is part of The Conversation’s coverage of COP26, the Glasgow climate conference, by experts from around the world.
Amid a rising tide of climate news and stories, The Conversation is here to clear the air and make sure you get information you can trust. Read more of The Conversation’s U.S. and global coverage.


