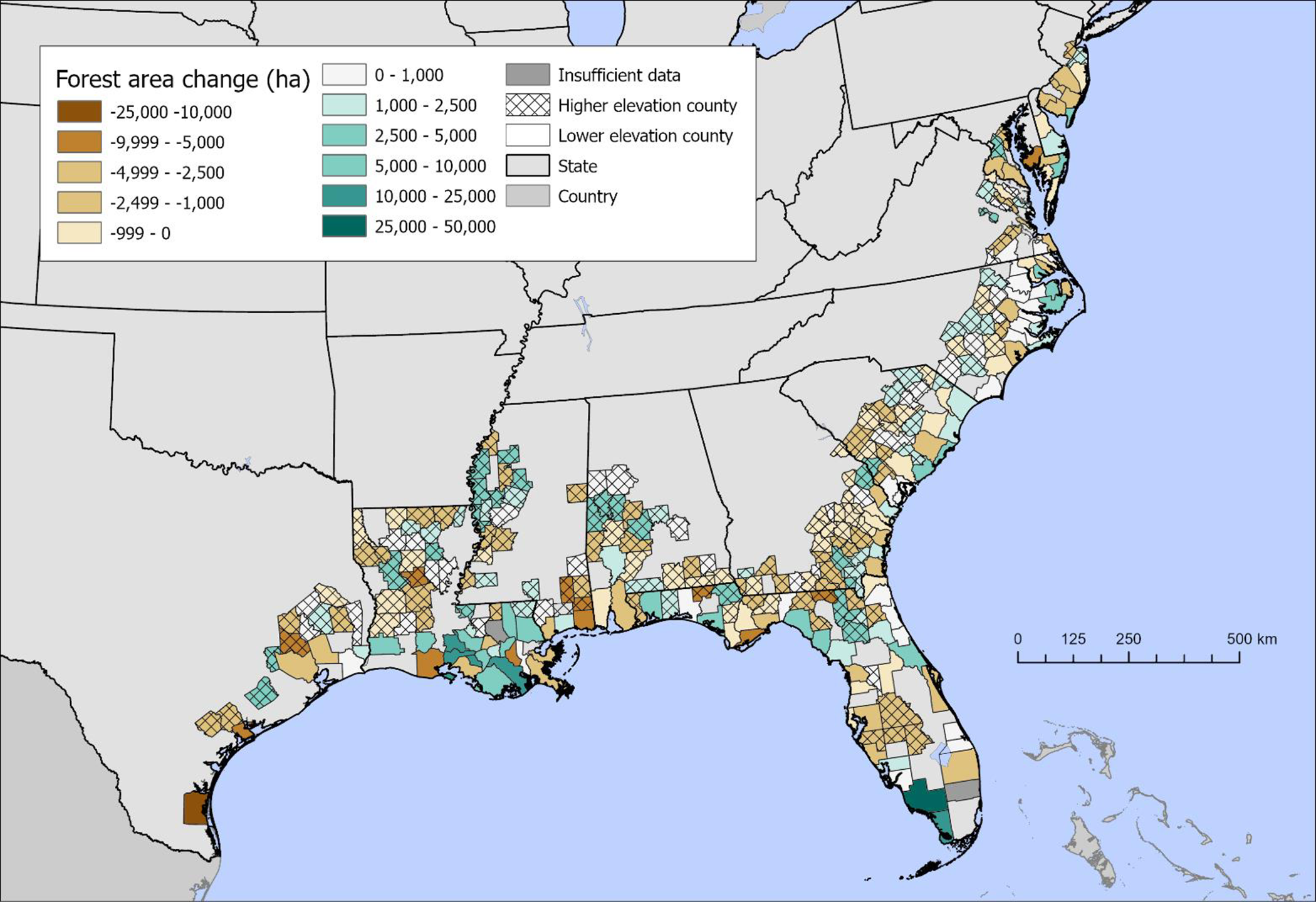
Map of change between sampling intervals in forest area for low and mid elevation (crossed) counties derived from the FIA. Vector shapefiles were retrieved from the U.S. Census Bureau.
Imagine driving along the coast and seeing rows of lifeless trees standing in pools of water—gray, leafless, and eerie. These “ghost forests” are appearing along the eastern United States, and they tell a sobering story about how climate change is reshaping our coastal landscapes. Coastal forests, which provide critical benefits to both people and wildlife, are disappearing or transforming at an alarming rate.
What Are Coastal Forests and Why Are They Important?
Coastal forests are unique woodlands found near the shorelines of oceans, bays, and estuaries. These forests thrive in areas with a mix of salty and fresh water, making them different from inland forests.
Coastal forests are essential for:
- Wildlife Habitat: They provide homes for birds, fish, and other animals that rely on both land and water ecosystems.
- Flood Protection: Their trees and soil act as natural barriers, absorbing water and reducing the impact of floods and storm surges.
- Carbon Storage: Coastal forests capture and store large amounts of carbon dioxide, which helps slow the pace of global warming.
These vital ecosystems are under threat. Rising sea levels, stronger storms, and higher temperatures are causing widespread damage. Many trees are dying, leaving behind ghost forests where thriving woodlands once stood.
How Climate Change Is Impacting Coastal Forests
Climate change is reshaping coastal forests in profound ways, driven by rising sea levels, stronger storms, and increasing temperatures. Each of these factors contributes to the gradual transformation of these ecosystems, creating significant challenges for their survival.
- Sea Level Rise: As sea levels rise, saltwater moves further inland, soaking the roots of trees that cannot survive in salty conditions. Over time, these trees die, creating ghost forests. Areas like the Chesapeake Bay have seen this transformation accelerate, as low-lying forests succumb to saltwater intrusion.
- Stronger Storms: Hurricanes and tropical storms are becoming more intense due to climate change. These storms knock down trees, flood forest areas, and create conditions that make it harder for new trees to grow. While some forests recover, many do not, leading to a permanent loss of trees and wildlife habitats.
- Warming Temperatures: Rising temperatures put stress on coastal forests by changing the types of trees and plants that can survive. Warmer weather can also make forests more vulnerable to pests and diseases, further accelerating tree loss.
What This Means for Us
The disappearance of coastal forests has far-reaching consequences that go beyond the trees themselves. From influencing the global climate to protecting communities and wildlife, these ecosystems play a critical role in maintaining balance.
- Carbon Storage: Coastal forests are powerful carbon sinks, meaning they absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When these forests die, they release this stored carbon back into the air, worsening global warming.
- Flood Protection: Without coastal forests, communities are more exposed to flooding and storm surges. These natural barriers are irreplaceable in their ability to protect homes, roads, and other infrastructure from water damage.
- Wildlife Impact: The loss of coastal forests means many animals lose their homes. Birds, amphibians, and fish that rely on these ecosystems are forced to relocate—or they may not survive at all.
What Can Be Done?
While the challenges facing coastal forests are significant, there are practical steps we can take to protect and restore these vital ecosystems. From preserving existing forests to adapting to the realities of climate change, these actions offer hope for the future.
1. Protect Existing Forests
Taking steps to safeguard the forests we still have is crucial for their survival.
- Limit construction and development near coastal areas to reduce stress on these ecosystems.
- Establish protected zones where forests can thrive without human interference.
2. Plant More Trees
Replanting trees native to the land can restore damaged forests and strengthen their resilience against climate change.
- Reforestation efforts can help rebuild damaged areas and increase the number of trees that store carbon.
- Focus on planting salt-tolerant species, native to the land, in vulnerable areas to adapt to rising sea levels.
3. Adapt to Climate Change
Adapting to the realities of climate change can help protect coastal forests and ensure their long-term survival.
- Build barriers or channels to prevent saltwater from reaching inland forests.
- Use technology and research to monitor changes in forest health and plan for future challenges.
Summing Up
Coastal forests are lifelines for wildlife, shields against floods, and crucial allies in the fight against climate change. Saving these forests matters, not only for the environment but also for the well-being of communities that rely on them. Conservation efforts and innovative solutions are helping some coastal forests recover. And, with collective action, we can ensure these vital ecosystems continue to thrive for generations to come.
Source: Ardón, M., Potter, K. M., White, E., Jr., & Woodall, C. W. (2025). Coastal carbon sentinels: A decade of forest change along the eastern shore of the US signals complex climate change dynamics. PLOS Climate, 4(1), e0000444. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pclm.0000444. See the data.


