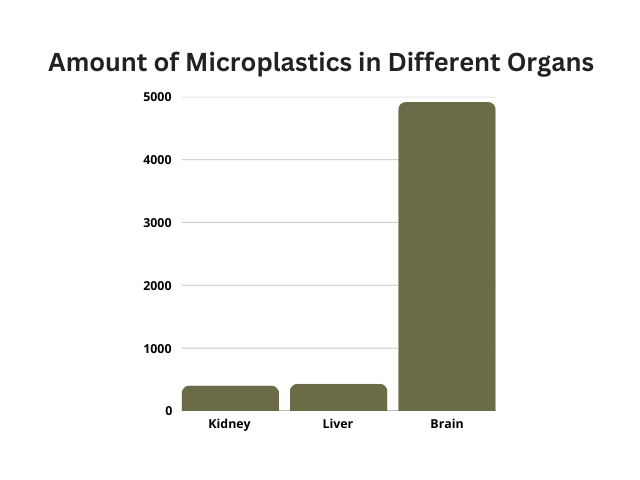
Microplastic Concentrations in Human Organs: Brain samples contained 7–30 times higher MNP concentrations than liver or kidney tissues. Median MNP concentration in the brain (2024 samples): 4,917 µg/g (range: 4,026–5,608 µg/g). Median MNP concentration in the liver (2024 samples): 433 µg/g. Median MNP concentration in the kidney (2024 samples): 404 µg/g.
Why Should We Care?
Plastic pollution is everywhere. Scientists have found microplastics in our food, drinking water, and even the air we breathe. But a new study has revealed something even more alarming—microplastics are accumulating in human brains!
Researchers found that brain samples contained up to 30 times more microplastics than other organs, raising concerns about long-term health risks. Even more shocking, people with dementia had five times the amount of microplastics compared to those without the disease.
What does this mean for our health? Let’s break it down.
What Did Scientists Find?
A team of researchers studied liver, kidney, and brain samples from people who had passed away. Using advanced technology, they found:
- All organs contained microplastics, but the brain had the highest levels—even more than the liver and kidneys, which naturally filter toxins.
- The most common type of plastic found was polyethylene (PE)—used in plastic bags, food packaging, and containers.
- The average microplastic concentration in the brain was 4,917 µg per gram of tissue—compared to 433 µg/g in the liver and 404 µg/g in the kidneys.
To put the quantity of microplastic concentration into perspective, imagine you’re filling three jars with sugar to represent the amount of microplastics in different organs:
- The kidney jar gets a small teaspoon (404 µg/g).
- The liver jar gets about the same—just over a teaspoon (433 µg/g).
- But the brain jar? You dump in more than 10 times that amount—nearly half a cup (4,917 µg/g)!
Now picture that sugar as tiny plastic shards instead of something sweet. Your brain—one of the most protected organs in your body—is absorbing these particles at a dramatically higher rate than the liver or kidneys, which are designed to filter out waste.
While other organs process and remove toxins, the brain seems to be holding onto plastic, potentially for life. Scientists still don’t know exactly what that means for long-term health, but they do know the levels are rising quickly, and that’s a cause for concern.
This is the first time scientists have confirmed that microplastics are accumulating in the human brain—a place that should be well-protected from foreign substances.
Why Is This a Big Deal?
Plastic doesn’t belong in our bodies, let alone inside our brains! Scientists are especially worried because:
Microplastics in the brain may contribute to neurological diseases. In people diagnosed with dementia, microplastic levels were over 26,000 µg per gram of brain tissue—more than five times higher than in non-dementia cases. These tiny plastics were found inside blood vessel walls and immune cells, suggesting they might be affecting brain function.
Microplastics can bypass the brain’s defense system. The blood-brain barrier normally protects the brain from harmful substances. This study suggests nanoplastics (as small as 100–200 nanometers) may be slipping through, raising concerns about how they could impact brain health over time.
While scientists haven’t proven that microplastics cause diseases like dementia, the fact that they are accumulating in the brain demands more research.
How Do Microplastics Get into Our Bodies?
You may not realize it, but we consume and inhale plastic particles every day. Here’s how they might be reaching our brains:
- Breathing in tiny plastic particles from dust, air pollution, and synthetic fabrics.
- Eating plastic-contaminated food—studies have found microplastics in seafood, salt, fruits, and vegetables.
- Drinking bottled water, which contains nearly double the amount of microplastics as tap water.
- Absorption through the bloodstream—scientists believe that some nanoplastics are small enough to pass through protective barriers in our bodies.
Once inside, these plastics don’t just disappear. They may stay trapped in organs like the liver, kidneys, and brain for years.
Has This Problem Gotten Worse?
Yes—dramatically. Scientists compared brain samples from 2016 and 2024 and found that:
- Microplastic levels in the brain have increased by nearly 50% in just 8 years.
- Similar increases were found in the liver and kidney, suggesting we are all being exposed to more plastic than ever before.
- Older brain samples (1997–2013) contained far fewer microplastics than recent ones, proving this is a rapidly growing problem.
With plastic production and pollution continuing to rise, scientists predict that microplastic exposure will only get worse unless major changes are made.
What Can We Do About It?
While the full health effects of microplastics are still unknown, reducing exposure is a smart move. Here’s how:
- Use fewer plastics: Switch to reusable bags, glass or metal water bottles, and cloth grocery bags.
- Filter your water: Some high-quality filters can remove microplastics from drinking water.
- Limit processed foods: Fresh, whole foods are less likely to contain microplastics than packaged and processed foods.
- Ventilate your home: Indoor air contains plastic particles from synthetic fabrics and household dust—keeping air clean can reduce inhalation.
- Support policies to reduce plastic pollution: Push for laws that limit plastic waste and promote better recycling solutions.
Summing Up
Microplastics are inside our brains, and their levels are rising at an alarming rate. Scientists don’t yet know the full impact on human health, but the findings from this study suggest a need for urgent action. While research continues, the best thing we can do is reduce plastic exposure and push for solutions to stop plastic pollution at its source.
The next time you drink from a plastic bottle or open a plastic-wrapped snack, remember—some of that plastic may never leave your body.
Would you like to see a future where our brains stay plastic-free? At activist360, we sure would!
Nihart, A. J., Garcia, M. A., El Hayek, E., Liu, R., Olewine, M., Kingston, J. D., Castillo, E. F., Gullapalli, R. R., Howard, T., Bleske, B., Scott, J., Gonzalez-Estrella, J., Gross, J. M., Spilde, M., Adolphi, N. L., Gallego, D. F., Jarrell, H. S., Dvorscak, G., Zuluaga-Ruiz, M. E., … & Campen, M. J. (2024). Bioaccumulation of microplastics in decedent human brains. Nature Medicine. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03453-1?error=cookies_not_supported&code=e505ad5b-107b-4753-ae03-68649bca94cd


