By Yuyu Zhou, The Conversation (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
The big idea
City lights that blaze all night are profoundly disrupting urban plants’ phenology – shifting when their buds open in the spring and when their leaves change colors and drop in the fall. New research I co-authored shows how nighttime lights are lengthening the growing season in cities, which can affect everything from allergies to local economies.
In our study, my colleagues and I analyzed trees and shrubs at about 3,000 sites in U.S. cities to see how they responded under different lighting conditions over a five-year period. Plants use the natural day-night cycle as a signal of seasonal change along with temperature.
We found that artificial light alone advanced the date that leaf buds broke in the spring by an average of about nine days compared to sites without nighttime lights. The timing of the fall color change in leaves was more complex, but the leaf change was still delayed on average by nearly six days across the lower 48 states. In general, we found that the more intense the light was, the greater the difference.
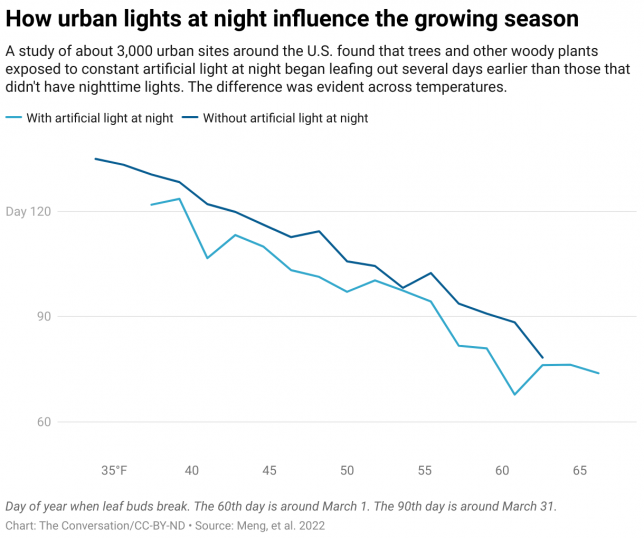
We also projected the future influence of nighttime lights for five U.S. cities – Minneapolis, Chicago, Washington, Atlanta and Houston – based on different scenarios for future global warming and up to a 1% annual increase in nighttime light intensity. We found that increasing nighttime light would likely continue to shift the start of the season earlier, though its influence on the fall color change timing was more complex.
Why it matters
This kind of shift in plants’ biological clocks has important implications for the economic, climate, health and ecological services that urban plants provide.
On the positive side, longer growing seasons could allow urban farms to be active over longer periods of time. Plants could also provide shade to cool neighborhoods earlier in spring and later in fall as global temperatures rise.
But changes to the growing season could also increase plants’ vulnerability to spring frost damage. And it can create a mismatch with the timing of other organisms, such as pollinators, that some urban plants rely on.
A longer active season for urban plants also suggests an earlier and longer pollen season, which can exacerbate asthma and other breathing problems. A study in Maryland found a 17% increase in hospitalizations for asthma in years when plants bloomed very early.
What still isn’t known
How the fall color timing will change going forward as night lighting increases and temperatures rise is less clear. Temperature and artificial light together influence the fall color in a complex way, and our projections suggested that the delay of coloring date due to climate warming might stop midcentury and possibly reverse because of artificial light. This will require more research.
How urban artificial light will change in the future also remains to be seen.
One study found that urban light at night had increased by about 1.8% per year worldwide from 2012-2016. However, many cities and states are trying to reduce light pollution, including requiring shields to control where the light goes and shifting to LED street lights, which use less energy and have less of an effect on plants than traditional streetlights with longer wavelengths.
Urban plants’ phenology may also be influenced by other factors, such as carbon dioxide and soil moisture. Additionally, the faster increase of temperature at night compared to the daytime could lead to different day-night temperature patterns, which might affect plant phenology in complex ways.
Understanding these interactions between plants and artificial light and temperature will help scientists predict changes in plant processes under a changing climate. Cities are already serving as natural laboratories.


