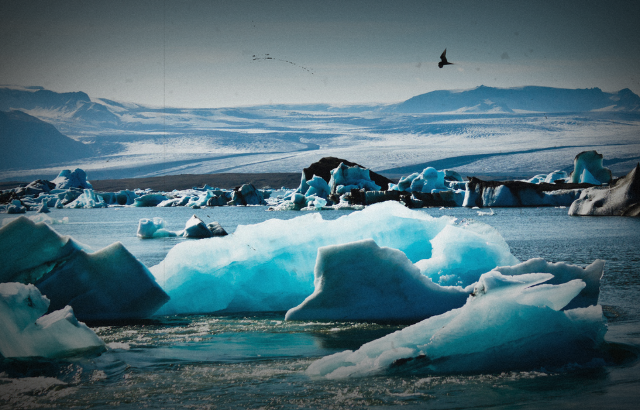
Photo of permafrost thawing with ominous darkening effect surrounding the photo.
New Research Unveils Risks of Mercury Mobilization in the Yukon River Basin Due to Permafrost Thaw
The Arctic is heating up faster than anywhere else on Earth, and this rapid warming is causing a lot of problems. One big concern is the melting of permafrost—ground that has been frozen for thousands of years. When this frozen ground thaws, it can release harmful substances into our environment. recent study published in Environmental Research Letters looked at how mercury, a toxic metal, is being released from permafrost in the Yukon River Basin in Alaska. This is bad news for the environment, and it could also affect our health.
Why Mercury in Permafrost is a Problem
Mercury is a dangerous metal that can poison living things, including humans. It’s especially harmful because it can build up in the food chain. For example, small fish absorb mercury from their environment, and when bigger fish eat those smaller fish, the mercury accumulates. If humans eat those bigger fish, they can get sick. Mercury has been locked away in permafrost for a long time, but as the Arctic warms and the permafrost melts, this mercury is being released.
What the Study Found
Researchers studied two areas in the Yukon River Basin: Huslia and Beaver. Here’s what they discovered:
- Mercury in the Soil: The study found that the soil in these areas contains mercury—about 49 nanograms per gram in Huslia and 39 nanograms per gram in Beaver. This may not sound like much, but it’s enough to be concerning, especially as it spreads into the environment.
- River Erosion Releases Mercury: As rivers in the Yukon River Basin move and change course, they erode the riverbanks, which releases mercury into the water. Some of this mercury gets washed away, while some gets redeposited in new locations. The study found that more mercury is released in some areas, like Beaver, while in others, like Huslia, more is deposited back into the ground.
- Impact on Communities and Wildlife: The release of mercury is especially dangerous for people who live in the Arctic and rely on fishing for food. When mercury enters the water, it can turn into a form that is even more toxic, called methylmercury. This can then build up in fish, which is a major part of the diet for many Indigenous communities in Alaska. Eating fish contaminated with mercury can lead to serious health problems.
Why This Matters
This study shows how climate change is not just about warmer temperatures—it’s also causing toxic substances to be released into our environment. The Yukon River Basin is a major waterway, and what happens here can affect larger ecosystems and even the Arctic Ocean. If we don’t address this issue, the mercury released from permafrost could have far-reaching effects on both wildlife and people.
What We Can Do
Understanding how climate change is impacting our world is the first step in taking action. This study highlights the importance of monitoring these changes and finding ways to reduce the risks. We need to pay attention to what’s happening in the Arctic and support efforts to protect our environment.
Summing Up
The melting of permafrost in the Yukon River Basin is releasing mercury into our environment, which poses serious risks to both nature and human health. As climate change continues to accelerate, it’s crucial that we understand these impacts and work together to find solutions. By staying informed and taking action, we can help protect our planet for future generations.
Call to Action
If you care about the environment and want to learn more about how climate change is affecting our world, read our weekly articles and follow us on X.com. Together, we can make a difference.
Study referenced: Smith, M. I., Ke, Y., Geyman, E. C., Reahl, J. N., Douglas, M. M., Seelen, E. A., Magyar, J. S., Dunne, K. B. J., Mutter, E. A., Fischer, W. W., Lamb, M. P., & West, A. J. (2024). Mercury stocks in discontinuous permafrost and their mobilization by river migration in the Yukon River Basin. Environmental Research Letters, 19(8), 084041.