Fluffy clouds and blue sky background. Credit: Photo by Engin Akyurt on Unsplash.
New Study Unveils Link Between Cloud Type, Precipitation and Air Quality Over Southern Ocean
The atmosphere over the Southern Ocean (SO) is noted for being exceptionally clean, largely untouched by anthropogenic or terrestrial emissions. This quality makes the SO an ideal natural laboratory for studying pre-industrial climate conditions and the interactions between aerosols, clouds, and precipitation.
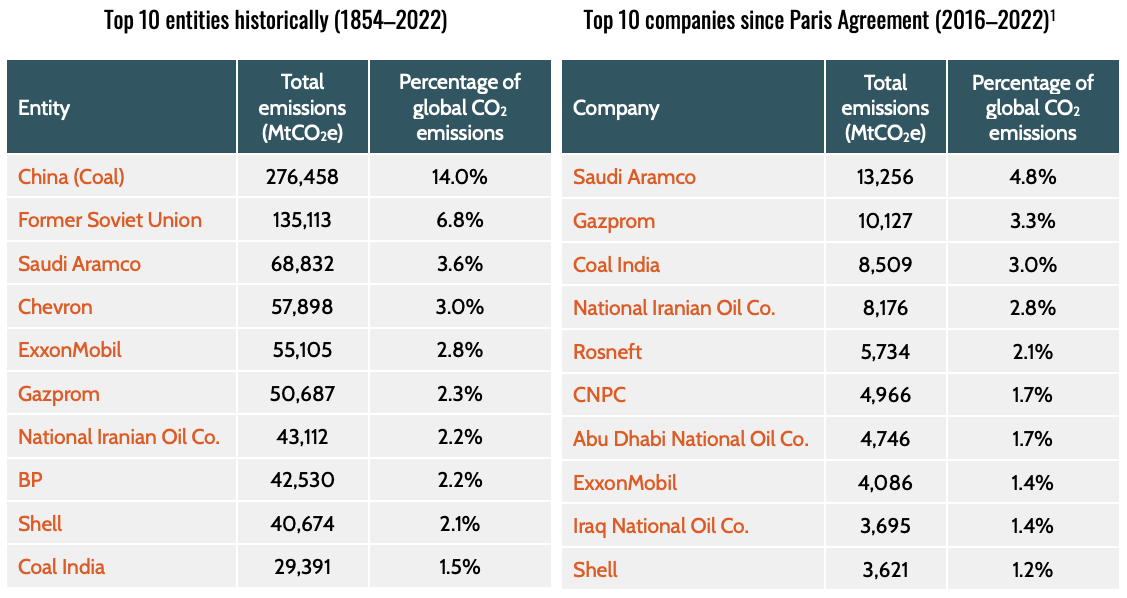
A recent study published in Nature delves into the intricacies of aerosol removal by precipitation. Researchers from Monash University, the Australian Research Council, and other institutions analyzed several years of observational data from the Kennaook/Cape Grim Observatory in Tasmania. They focused on two distinct cloud patterns: open puffy mesoscale cellular convection (MCC) and closed flat MCC. Here are the key takeaways from the study:
Key Findings
- Cloud Type and Rainfall: The study found that open, puffy clouds produced heavier and more frequent rainfall (1.72 mm per day, occurring around 17% of the time) compared to closed, flat clouds (0.29 mm per day, occurring only 4.5% of the time).
- Connection to Air Quality: Surprisingly, the researchers observed lower levels of tiny particles (called cloud condensation nuclei or CCN) in the air during periods when open, puffy clouds dominated (69 particles per cubic centimeter) compared to when closed, flat clouds dominated (89 particles per cubic centimeter). This suggests that the heavier rainfall from open clouds may be “cleaning out” the atmosphere through a process called wet deposition.
- Seasonal Variations: The inverse relationship between rainfall and CCN levels held true across different seasons, with the most pristine air observed during the winter months when open clouds dominated. The study also noted that open clouds were most frequent during the winter. These cycles suggest a robust interplay between the oceanic emissions and the atmospheric conditions over the year.
- Weather Influences: The study highlighted the crucial role played by weather factors, such as atmospheric stability and surface air pressure patterns, in influencing the cloud shape, rainfall rates, and ultimately, the observed CCN levels.
- Daily Cycle: Interestingly, while rainfall peaked in the early morning hours, the CCN cycle was out of phase, suggesting that weather factors, rather than CCN levels, were the primary drivers of the daily rainfall cycle.
These findings underscore the complex interplay between clouds, precipitation, and aerosols in the remote Southern Ocean region. The study suggests that the heavier precipitation from open cellular cloud patterns may be removing or washing out more particles from the atmosphere.
Implications for Climate Models
The detailed observation of wet deposition mechanisms and their interaction with CCN offers valuable insights into cloud formation and precipitation processes. These insights help refine climate models, particularly in predicting the radiative balance and hydrological responses of the earth’s system under varying climatic conditions.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how aerosols, clouds, and precipitation interact over the Southern Ocean is important because it helps improve climate models, making them better at predicting weather and climate changes. This is important for humanity to enhance our ability to prepare for and adapt to future environmental changes and extreme weather events, which can have significant impacts on agriculture, water resources, and overall human well-being.
Source: Alinejadtabrizi, T., Lang, F., Huang, Y., Ackermann, L., Keywood, M., Ayers, G., Krummel, P., Humphries, R., Williams, A. G., Siems, S. T., & Manton, M. (2024). Wet deposition in shallow convection over the Southern Ocean. npj Climate and Atmospheric Science.