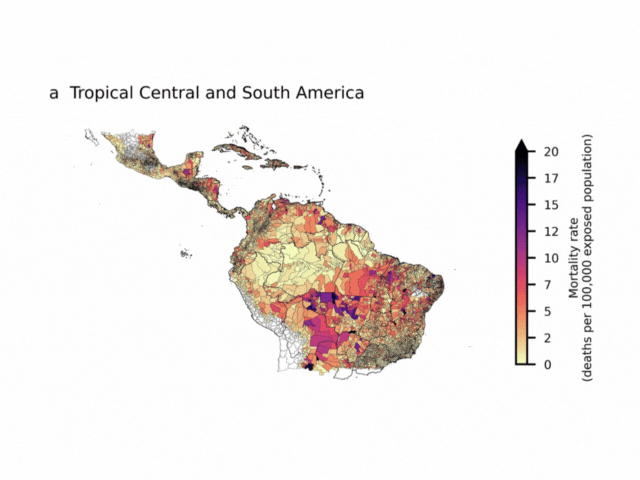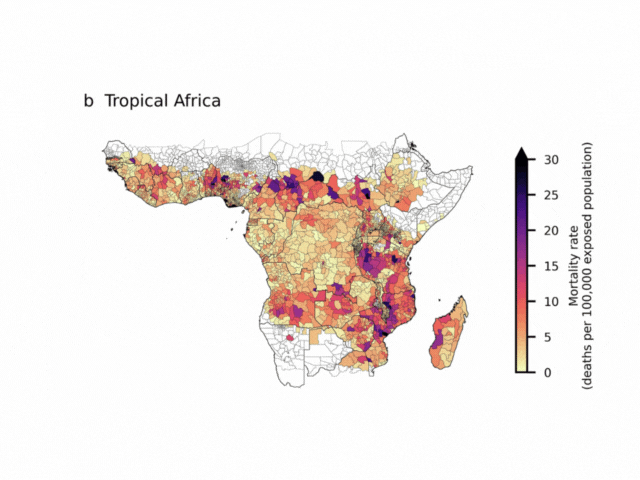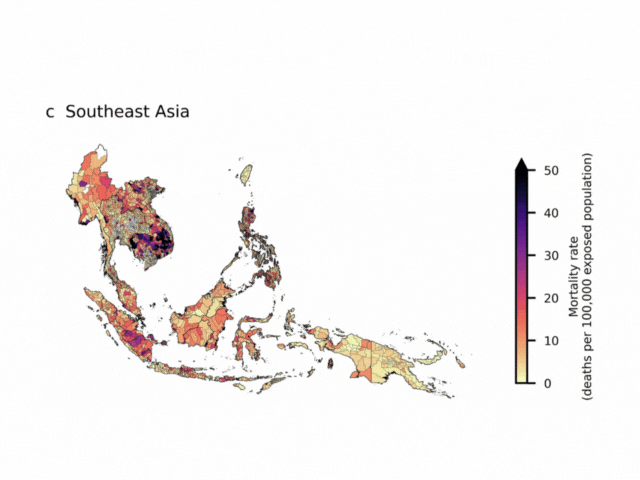
The maps show regions of Tropical Central and South America (a), Tropical Africa (b), and Southeast Asia (c). Colours show number of deaths per year per 100,000 people located in areas of forest loss (central estimate), aggregated by second-level administration divisions. Boundaries for second-level administration divisions are from GADM (https://gadm.org/index.html).
When we hear about deforestation, many of us think first about disappearing wildlife, endangered species, or the loss of carbon storage that slows climate change. All of that is true, but there’s another hidden danger. Cutting down tropical forests hurts our planet’s biodiversity and directly affects human health. New research shows that losing forests makes people hotter, sicker, and in many cases, more likely to die from extreme heat.
What the Study Found
A recent study published in Nature Climate Change looked at forest loss across the tropics between 2001 and 2020. The researchers found that when forests are cleared, the land surface warms up quickly. On average, deforested areas became almost 0.5 °C hotter than places that kept their trees.
That may not sound like much, but for people living in already hot, humid places, even small increases can push temperatures past safe limits. The study estimated that about 345 million people have been exposed to this extra warming caused by deforestation. That’s nearly the size of the entire U.S. population.
The Human Toll
The warming from deforestation is deadly. According to the study, deforestation is linked to about 28,000 extra heat-related deaths each year (Reddington et al., 2025). These deaths happen because the body can only handle so much heat before heart, lung, or kidney problems set in.
Some of the hardest-hit regions include:
- Indonesia, Vietnam, and Malaysia, where heat deaths per 100,000 people are among the highest in the world.
- Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo, which also face significant impacts.
- Southeast Asia overall, which accounts for more than half of all the deaths linked to deforestation-related heat.
In these countries, outdoor workers, such as farmers and construction workers, are especially vulnerable.
Why the Tropics Are Vulnerable
The tropics, regions close to the equator, are home to over 3.5 billion people. Many of these communities depend on outdoor work for their livelihoods. When forests are cut, not only does the land heat up, but shade disappears too. That makes outdoor work far more dangerous.
Health care access also plays a big role. In many tropical nations, hospitals and clinics are already under pressure, and people may not have reliable access to air conditioning, cooling centers, or emergency care. This limited ability to adapt means heat has a bigger impact on vulnerable groups, such as children, older adults, and outdoor workers.
Other Hidden Dangers
Heat isn’t the only risk linked to cutting forests. Deforestation also leads to:
- Air pollution from fires: When forests are burned, smoke can spread across entire regions. In past years, haze from Indonesian forest fires exposed tens of millions of people to unsafe air, leading to thousands of premature deaths.
- Spread of diseases: Clearing forests can increase the spread of diseases like malaria. In some places, standing water left after logging creates ideal breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
Together, these risks make deforestation not only an environmental problem but also a serious public health issue.
What Can Be Done
The good news is that protecting forests can prevent many of these heat-related deaths. Keeping trees standing provides shade, keeps local areas cooler, and reduces harmful smoke. On a larger scale, forests act as a buffer against climate change by storing carbon and releasing moisture into the air.
Steps that can help include:
- Stronger protections for tropical forests through laws and enforcement.
- Community-led conservation that involves local and Indigenous groups who know the land best.
- Investment in health systems and cooling strategies to protect people who already live in areas affected by deforestation.
- Global cooperation to reduce demand for products linked to deforestation, such as unsustainable palm oil, soy, and beef.
These actions can save thousands of lives each year.
Summing Up
The study’s message is clear: tropical forests aren’t just “carbon sinks” or wildlife havens. They are lifelines for millions of people. Losing them raises local temperatures, increases the risk of deadly heat, and harms human health in ways many of us never considered.
By protecting tropical forests, we preserve ecosystems while protecting people. Safeguarding these forests is a direct investment in healthier, safer communities around the world.
Source: Reddington, C. L., Smith, C., Butt, E. W., Baker, J. C. A., Oliveira, B. F. A., Yamba, E. I., & Spracklen, D. V. (2025). Tropical deforestation is associated with considerable heat-related mortality. Nature Climate Change. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-025-02411-0


