A conceptual illustration depicting human cognition, featuring a vintage anatomical drawing of a brain within a simple silhouette of a head.
What You Need to Know and How to Reduce Your Exposure
Did you know that tiny plastic particles—called microplastics—are in our food, water, and even the air we breathe? Every day, we are unknowingly consuming and inhaling microplastics. Scientists have now discovered something even more concerning: microplastics are making their way into human brains, and their levels are increasing.
This raises an important question: What does this mean for our health, and what can we do about it? While we may not be able to eliminate microplastics entirely, there are simple steps we can take to reduce our exposure and protect our health. In this article, we’ll break down what microplastics are, how they enter our bodies, the potential health risks, and practical ways to reduce our exposure.
What Are Microplastics?
Microplastics are tiny plastic particles, smaller than 5mm, that come from broken-down plastic waste, synthetic clothing, industrial processes, and food packaging. Because plastic never fully biodegrades, these particles remain in the environment indefinitely, breaking down into even smaller pieces over time.
Common Sources of Microplastics
Microplastics are found in everyday items, including:
- Bottled water: Contains significantly more microplastics than tap water.
- Seafood: Marine animals ingest microplastics from polluted oceans.
- Processed foods: Particularly those packaged in plastic.
- Tea bags: Some brands use plastic-based tea bags that release billions of plastic particles into hot water.
- Air: Microplastics are floating around in household dust and city pollution.
Since we eat, drink, and breathe microplastics daily, it’s important to understand how they enter our bodies and what harm they may cause.
How Do Microplastics Get into the Human Body?
Microplastics make their way into our bodies through three primary routes:
Eating and Drinking
- Bottled water drinkers ingest up to 90,000 microplastic particles per year, compared to 4,000 for tap water drinkers (Cox et al., 2019).
- Seafood, processed foods, and canned goods can contain microplastics due to contamination during production and packaging.
- Heating food in plastic containers releases billions of plastic particles into the food.
Breathing
Airborne microplastics are present in the air we breathe at home, in offices, and outdoors, particularly in urban areas. Additionally, synthetic clothing sheds plastic fibers into the air when it is washed or worn, further contributing to the inhalation of these particles.
Household Exposure
Cooking and storing food in plastic can cause microplastics to leach into the food we eat. Similarly, plastic tea bags and coffee pods release billions of tiny plastic particles into hot liquids, increasing overall exposure.
Because these tiny particles are everywhere, scientists are now studying how they affect our health—especially our brains.
Are Microplastics Harmful to Our Health?
While research is still ongoing, several studies have raised serious concerns about microplastics in the human body. Here’s what scientists have found so far:
Microplastics in the Brain
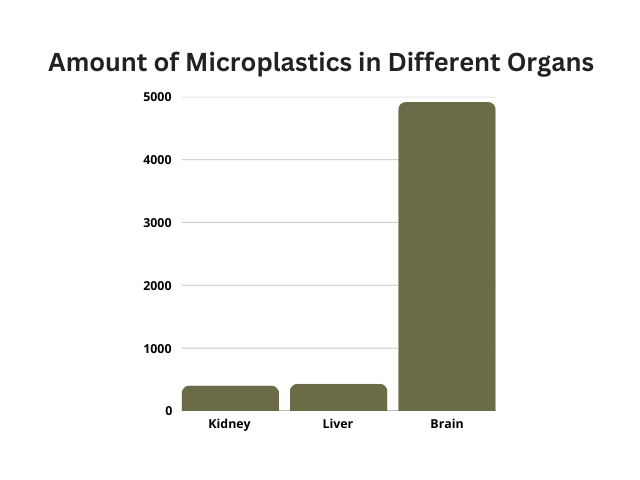
A recent study found microplastics in human brain tissue, with levels 3–5 times higher in people with dementia (Nihart et al., 2025). Scientists are unsure whether dementia weakens the brain’s defense, allowing more plastic in, or if microplastics contribute to cognitive decline.
Heart Disease Risk
A study found that people with plastic particles in their arteries had a higher risk of heart attacks and strokes (Marfella et al., 2024).
Gut Health Concerns
People with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) had 1.5 times more microplastics in their stool compared to healthy individuals (Yan et al., 2022). Microplastics may disrupt gut bacteria and contribute to inflammation.
Other Potential Effects
Scientists suspect microplastics may also contribute to:
- Hormone disruption: some plastics contain chemicals that interfere with the endocrine system.
- Lung irritation: from inhaling airborne microplastics.
- Long-term health risks: still being studied.
Since avoiding microplastics completely is impossible, the next best step is reducing exposure where we can.
Easy Ways to Reduce Microplastic Exposure
While plastic is everywhere, simple daily changes can significantly lower the amount of microplastics we ingest and inhale.
- Switch to Tap Water: Drinking tap water instead of bottled water can reduce microplastic intake by over 90%. Use a water filter if concerned about contaminants.
- Avoid Heating Food in Plastic: Use glass or stainless steel containers instead of plastic. Never microwave food in plastic containers.
- Choose Fresh or Frozen Foods Over Canned: Canned foods can release chemicals like BPA, which is linked to hormone disruption. Opt for fresh, frozen, or glass-packaged alternatives.
- Use Cloth or Metal Tea Strainers: Avoid plastic tea bags—opt for loose-leaf tea with a stainless steel infuser.
- Improve Air Quality: Use a HEPA air filter at home to remove airborne microplastics. Vacuum regularly to reduce plastic dust indoors.
These small changes can make a big difference in reducing everyday exposure.
Can Microplastics Be Removed from the Body?
Right now, scientists don’t know if microplastics can be fully removed from the human body, but some early research suggests:
- Sweating may help: Some studies suggest that sweating (through exercise or sauna use) can help excrete plastic-related chemicals like BPA.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Staying hydrated, eating fiber-rich foods, and regular exercise may help the body naturally eliminate toxins.
- Long-term exposure reduction: The best strategy is reducing intake in the first place.
More research is needed, but reducing microplastic exposure now is the safest approach.
Small Changes Make a Big Difference
Microplastics are everywhere, and while we can’t avoid them completely, we can take practical steps to limit exposure and protect our health. By making the choices we suggested above, you can help protect your health while also reducing plastic pollution in the environment.
It’s crucial to hold local, state, and national elected officials accountable for policies that protect your health and the well-being of your loved ones. Be mindful of who you vote for, and once they are in office, advocate for strong regulations that reduce plastic pollution and safeguard public health. Your voice matters—demand action.
Sources: Nihart et al., 2025 – Study on microplastics in the human brain (Nature Medicine). Marfella et al., 2024 – Microplastics and heart disease (New England Journal of Medicine). Cox et al., 2019 – Microplastic consumption (Environmental Science & Technology).