
Pollution emitter. Photo by Marcin Jozwiak on Unsplash
Carbon Majors: 57 fossil fuel and cement producers linked to 80% of global fossil CO2 emissions since the Paris Agreement
The Carbon Majors Database: Launch Report, a new comprehensive analysis conducted by InfluenceMap sheds light on the substantial impact that a small group of carbon-producing entities has on global CO2 emissions. This enlightening study traces back to 1854, identifying 117 producers responsible for a staggering 88% of global CO2 emissions from fossil fuels and cement between 2016 and 2022. This revelation comes post-Paris Agreement, underscoring the paradox of increased fossil fuel production amidst global pledges for emission reduction.
The Carbon Majors Database
The Carbon Majors Database, initially developed by Richard Heede of the Climate Accountability Institute and now hosted by InfluenceMap, offers an astonishing look into the historical emissions of the world’s largest oil, gas, coal, and cement producers. By categorizing these entities into investor-owned, state-owned, and nation-states, the database highlights the disproportionate role these entities play in driving global CO2 emissions.
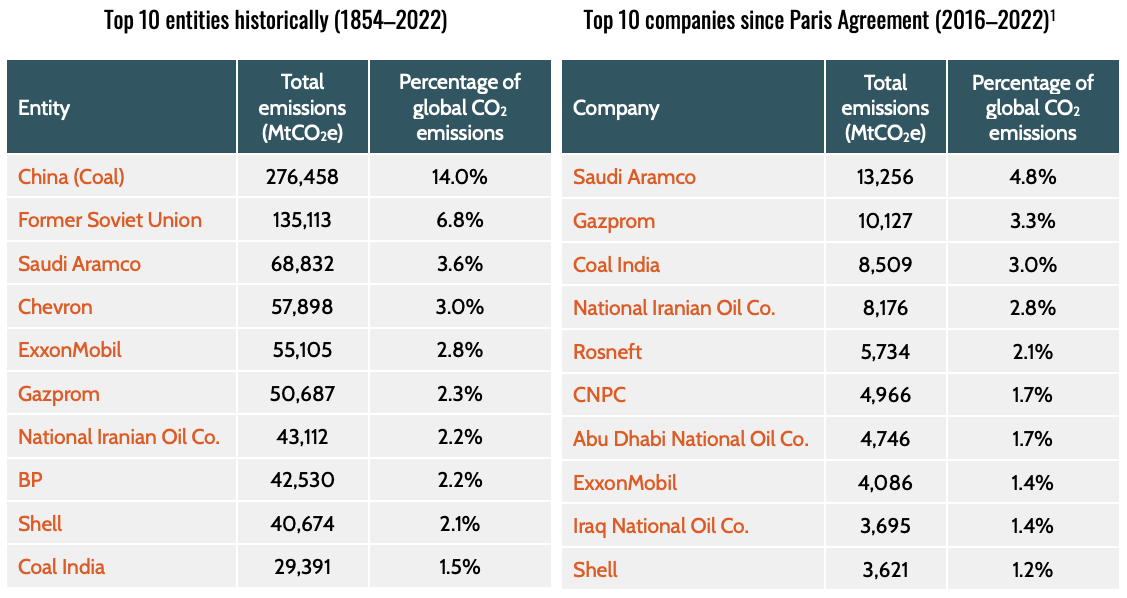
Top 10 entities global fossil CO2 emitters historically (1854–2022) and since Paris Agreement (2016–2022). Source: The Carbon Majors Database Launch Report, April 2024 by InfluenceMap.
The database reveals that 57 corporate and state entities linked to fossil fuel and cement production are responsible for 80% of the global emissions from 2016 through 2022. This period, notably after the Paris Agreement, has seen most fossil fuel companies ramp up their production, indicating a glaring misalignment with global climate goals.
The analysis underscores a troubling trend: the majority of fossil fuel companies have increased their production post-Paris Agreement, with a notable rise in emissions from Asian and Middle Eastern producers. This contradicts the global consensus on reducing fossil fuel dependence to mitigate climate change impacts.
Accountability and Climate Change
The report’s findings have implications in legal, regulatory, and academic contexts, offering a basis for holding fossil fuel producers accountable for their climate-related impacts. It emphasizes the need for corporate entities to align their operations with climate science and contribute to global emission reduction efforts.
A key insight from the report is the shift in coal production from investor-owned to state-owned entities, contributing to an increase in global coal consumption. This shift poses challenges to global emission reduction efforts, highlighting the need for comprehensive policies to address state-owned entities’ roles in coal production.
The report provides a granular look at emissions trends across different regions, with Asia and the Middle East experiencing significant increases in fossil fuel production and emissions. Conversely, North America and Europe show a more moderate trend, reflecting diverse global approaches to energy production and climate policy.
Final Thoughts
The Carbon Majors Report is a clarion call for immediate action against the entities most responsible for the climate crisis. There is an urgent need for global cooperation to halt the expansion of fossil fuel production and ensure a just transition to renewable energy sources. It underscores the imperative of global cooperation and corporate accountability in the pursuit of a sustainable future, emphasizing the role of data-driven analysis in informing policy and advocacy efforts.
Source: The Carbon Majors Database Launch Report, April 2024 by InfluenceMap.

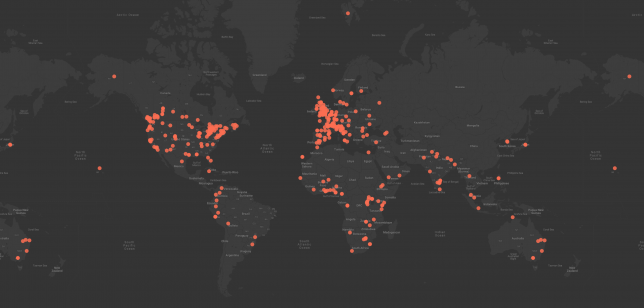 On September 15-17, millions marched around the world demanding an immediate, equitable end to fossil fuels.
On September 15-17, millions marched around the world demanding an immediate, equitable end to fossil fuels.