The UN Secretary-General, António Guterres, has launched the “Early Warnings for All” initiative, slated for completion by 2027, to develop advanced, multi-hazard, and people-centered early warning systems to protect every individual globally.
The “Early Warnings for All” Initiative
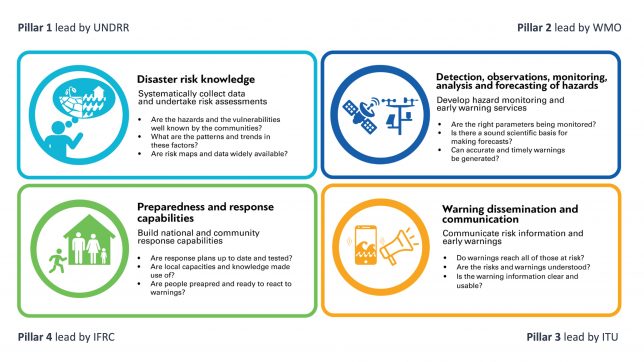
Initiated in March 2022 and with an action plan unveiled in November 2022, it’s founded on four pillars:
- Disaster risk knowledge, led by the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR).
- Detection, observations, monitoring, analysis, and forecasting of hazards, led by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
- Warning dissemination and communication, led by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
- Preparedness to respond, led by the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC).
Despite the proven efficacy of such systems in mitigating disaster impacts, access is limited, especially in underdeveloped and small island nations. The initiative requires $3.1 billion over five years and is endorsed by Multilateral Development Banks, emphasizing its role in mitigating climate impacts and protecting lives, livelihoods, and environments.
The initiative, seeking collaborations across sectors and levels, aims to modernize global early warning systems and align them with climate action goals, focusing on integrity and justice. The systems will provide understandable and actionable warnings, enabling timely actions to minimize potential harm, especially in vulnerable regions like Africa, where 60% lack coverage. Investments of $800 million in developing countries could potentially avert $3-16 billion in losses annually. It represents a collective effort to safeguard vulnerable populations and emphasizes the importance of united actions in realizing the goals of this initiative.
Harnessing Data and AI in a Unified Response to Crises
In light of the multifaceted global crises exacerbated by climate change, advancements in AI, technologies, and data ecosystems offer transformative solutions. At the 78th UN General Assembly, discussions included harnessing technological breakthroughs for a resilient future and unlocking the potential of data, analytics, and AI to anticipate and mitigate crises and disasters. Emphasizing the need for innovative data-driven approaches, the discussions revolved around global initiatives like the Early Warnings for All initiative and the Global Climate Action Agenda, underlining collective efforts to build a more resilient world and achieve Sustainable Development Goals, aiming to leave no one behind.
The UN’s “Early Warnings for All” initiative exemplifies a collective stride towards global resilience and inclusive crisis response. It highlights a united commitment to employ innovative technologies, data analytics, and AI to lessen the impacts of climate change and disasters, especially for the vulnerable. This initiative symbolizes a united vision for a sustainable and equitable future, aiming to ensure security and well-being for all, emphasizing a future where every individual is accounted for and protected.

 On September 15-17, millions marched around the world demanding an immediate, equitable end to fossil fuels.
On September 15-17, millions marched around the world demanding an immediate, equitable end to fossil fuels.