Navigating the Crowded Cosmos
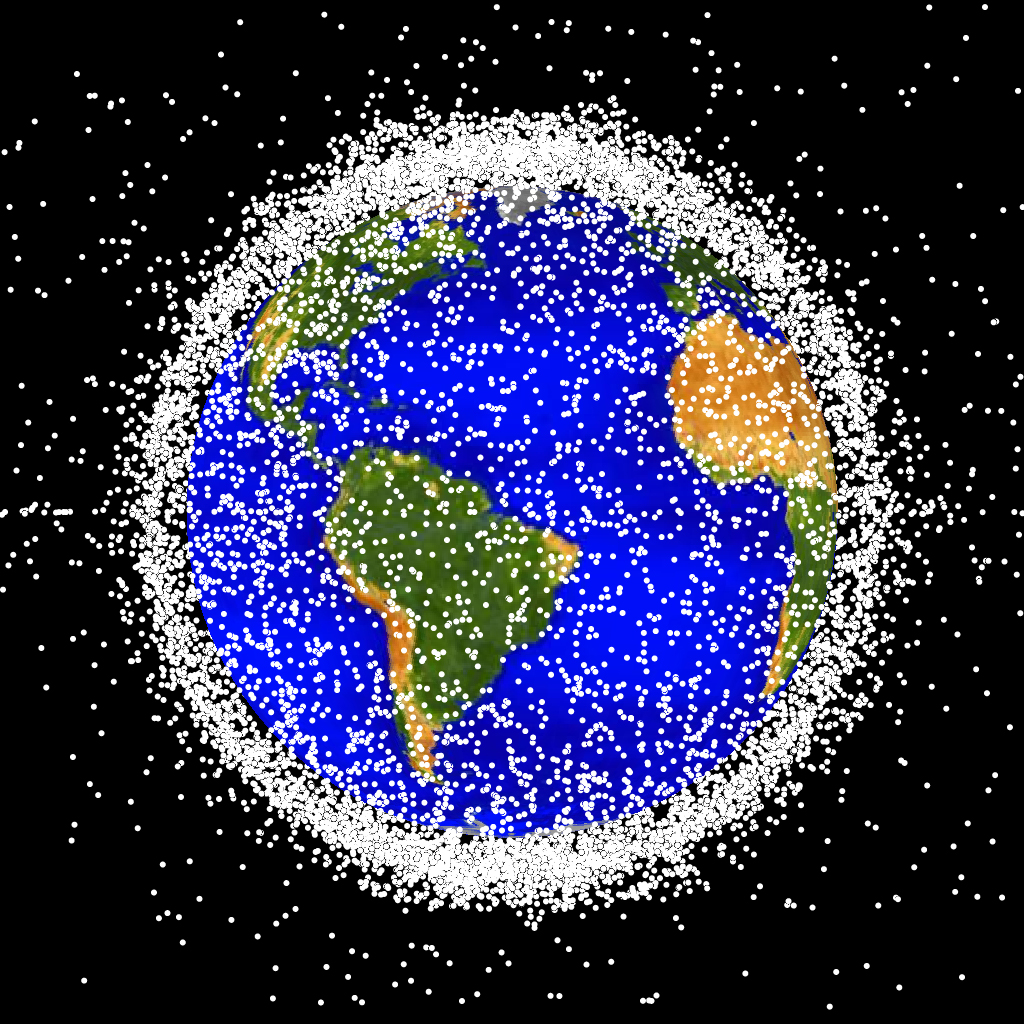
As the Earth’s orbital space becomes increasingly populated with satellites crucial for scientific research, communication, and navigation, the burgeoning issue of space debris poses a threat to our sustainable future in space. The ESA’s 2023 Space Environment Report casts a sobering light on the crowded and hazardous orbits, underlining the urgency for effective space debris mitigation measures.
The Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee’s guidelines set forth in 2002, aimed at reducing space debris, have become the foundation for space policy. However, with a record-breaking 2,409 new satellites launched in 2022, these guidelines are being outpaced by the sheer volume of space traffic. Many satellites remain in their operational orbits post-mission, creating potential debris clouds that could linger for years. With the rise of commercial satellite constellations in low-Earth orbits, the risk of collisions has grown exponentially, necessitating more frequent collision avoidance maneuvers.
Despite improvements in adopting debris mitigation measures, the ESA report suggests that current efforts are insufficient given the rate of satellite launches and existing debris. Over half of the 30,000 tracked debris pieces are cluttering low-Earth orbit, which doesn’t account for the countless smaller, untracked objects. The report warns that if we continue on this path, the dream of a sustainable space environment could slip through our fingers.
A Silver Lining
Nevertheless, there is a silver lining. A record number of satellites and fragments reentered Earth’s atmosphere in 2022, showing that adherence to guidelines — like vacating protected orbits within 25 years of end-of-life — is improving. Moreover, more than 80% of constellation satellites are now designed to deorbit within two years post-mission. Yet, most of these reentries are uncontrolled, posing risks of debris landing unpredictably on Earth.
ESA’s proactive steps include the novel “assisted reentry” technique, successfully demonstrated with the Aeolus satellite, and pioneering the ClearSpace-1 mission for active debris removal. These initiatives are part of ESA’s Zero Debris goal for 2030, aiming to leave no new space debris in critical orbits. By setting a precedent with the ClearSpace-1 mission, ESA aspires to catalyze a new commercial sector focused on debris removal and promote sustainable space operations industry-wide.
Time to Act
The 2023 report from ESA serves as a call to action for the global space community. The space around our planet is a finite, invaluable resource that demands our immediate attention and stewardship to prevent the dire predictions of Kessler Syndrome from becoming a reality.
…. fragments from future collisions will be generated faster than atmospheric drag will remove them.”
The Kessler Syndrome, as discussed by Donald J. Kessler, March 8, 2009
With continued focus and innovation in space sustainability, we can ensure that the benefits of space advancements are not overshadowed by the growing cloud of orbital debris. It’s time to act and safeguard our space environment for future generations.
